How to Cite
Share
Abstract
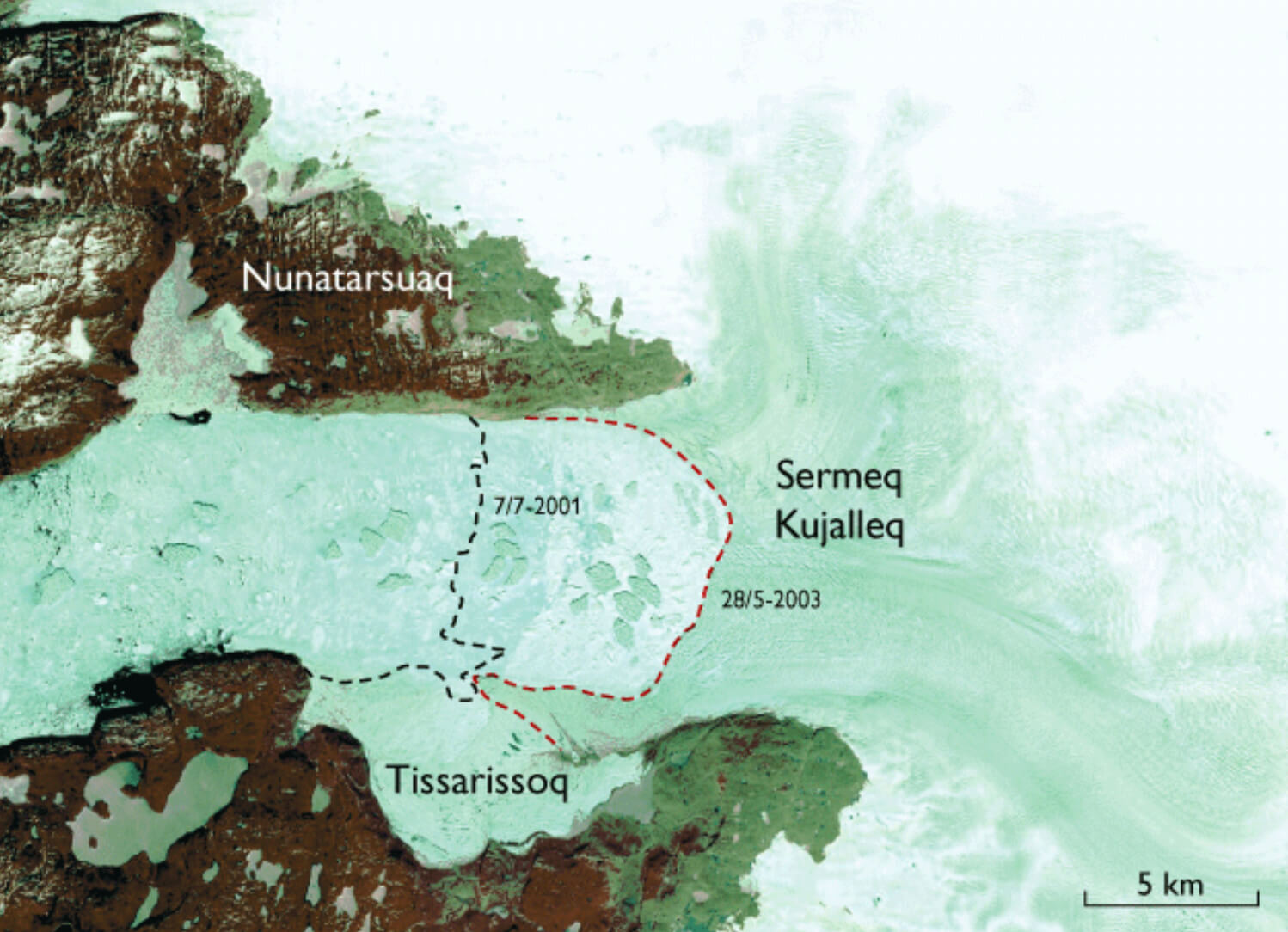
Jakobshavn Isbræ (also known as Sermeq Kujalleq or Ilulissat Isbræ) is situated at about 69°10′N and 50°00′W in West Greenland. This major outlet from the Inland Ice has an extremely high rate of movement (nearly 1 m/hour) and thus a high production of icebergs, which via the icefjord float westwards through Disko Bugt to Davis Strait (Fig. 1). Estimates of the iceberg production are in the range of 35 ± 10 km3 ice per year, more than 10% of the entire calf-ice production of the Inland Ice (e.g. Bauer l968; Bindschadler 1984). The icefjord into which Sermeq Kujalleq calves is Kangia, best known in glaciological literature as Jakobshavn Isfjord. Spectacular changes of the glacier were observed during 2002 and 2003 at the same time as it was nominated for inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List under the name ‘Ilulissat Icefjord’.
How to Cite
Share
Downloads
Editors: Martin Sønderholm & A.K. Higgins
The Review of Survey activities presents a selection of 23 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, from the microbial to the plate tectonic level.
The Survey's activities in Denmark are documented by ten papers. These include discussion of the [...]










