How to Cite
Share
Abstract
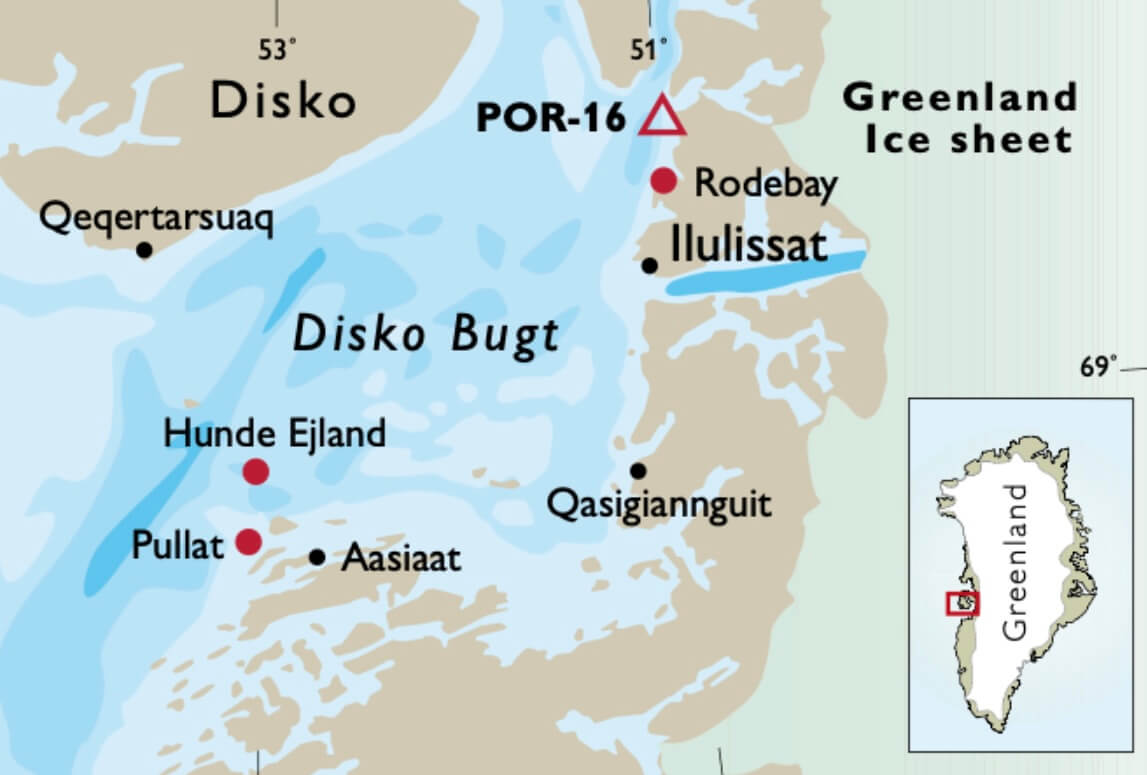
The European trading and whaling activities of the 17th– 19th centuries provide records of climate and sea- ice conditions off West Greenland in the form of ships’ logs and other official documents in many archives around Europe. These documents, combined with evidence from marine sediments, help describe climate changes in general, and seaice volume changes in particular, in connection with human activity in the region. The Greenland National Museum & Archives in Nuuk (NKA) hosts a unique collection of original documents presenting detailed insight into weather and ice conditions as well as the daily life of the colonial centres and outposts recorded by the documents of the Danish administration. These documents also reveal many aspects of the interaction between the Inuit and Europeans from 1779 onwards. Information retrieved from the archives in Nuuk has been combined with results from palaeo-environmental investigations of marine sediment cores to unravel climate variability and changes in sea ice. This information has been supplemented with data from an extensive field programme using drones to document onshore remains from the whaling period in the Disko Bugt region (Fig. 1).
How to Cite
Share
Downloads
Editors Adam A. Garde, Ole Bennike and W. Stuart Watt
The 22 contributions in this issue of Review of Survey activities demonstrate the broad field of activities performed by the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland and external partners.
Seven papers on Danish geology comprise an investigation of reservoir sandstones for oil [...]










