How to Cite
Share
Abstract
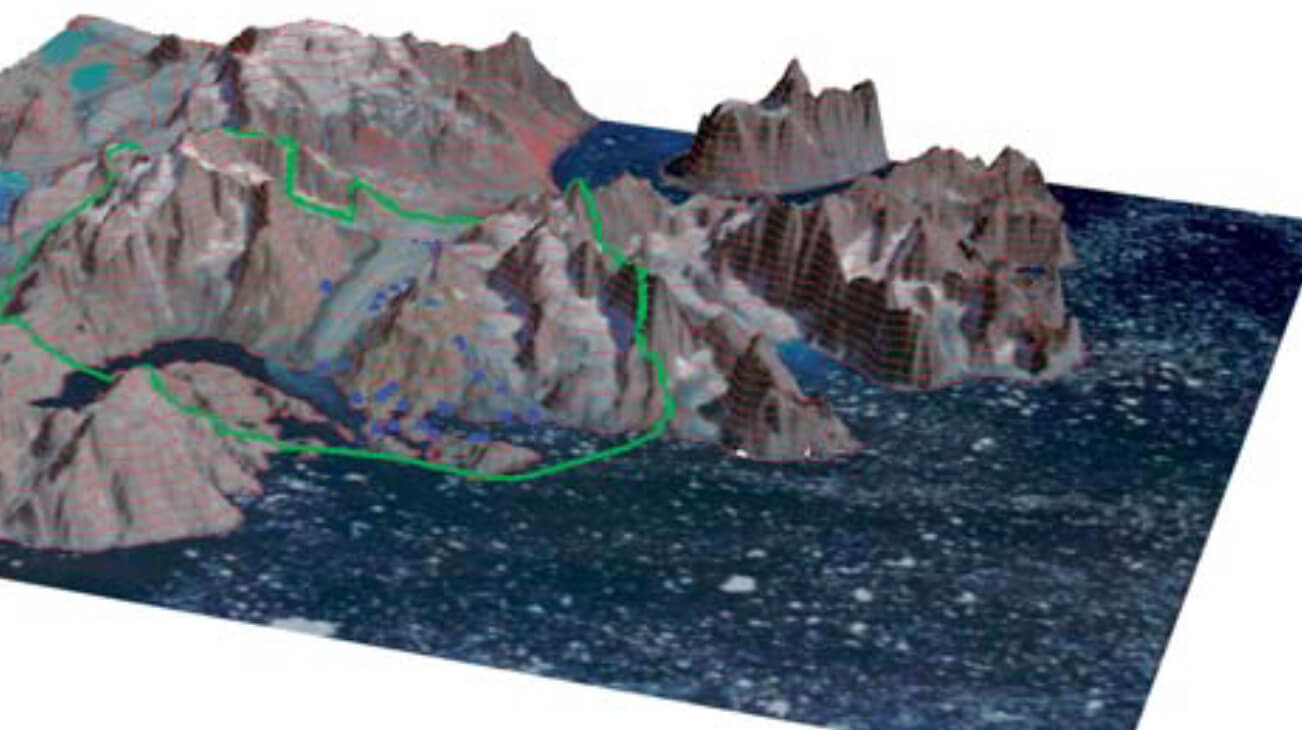
The Skaergaard intrusion (Fig. 1) is probably the most studied layered gabbro intrusion in the world (Wager & Deer 1939; Wager & Brown 1968; McBirney 1996; Nielsen 2004). The intrusion is c. 54.5 Ma old and was formed during the Palaeogene opening of the North Atlantic Ocean, intruding into the base of the East Greenland flood basalts. The intrusion is relatively small with a volume of c. 300 km3 (Nielsen 2004). Spectacular magmatic layering and systematic evolution in the compositions of liquidus phases and estimated melt compositions (e.g. Wager & Brown 1968) have made the intrusion the most studied example of the development of the ‘Fenner trend’ of iron enrichment in basaltic liquids (e.g. Thy et al. in press; Veksler in press).
How to Cite
Share
Copyright (c) 2009 Troels F.D. Nielsen, Símun D. Olsen, Bo M. Stensgaard

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Edited by Ole Bennike, Adam A. Garde and W. Stuart Watt
This Review of Survey activities presents a selection of 19 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, including field-based, laboratory and remote sensing studies.
The Survey's activities in Denmark are illustrated by ten articles covering the [...]









