How to Cite
Share
Abstract
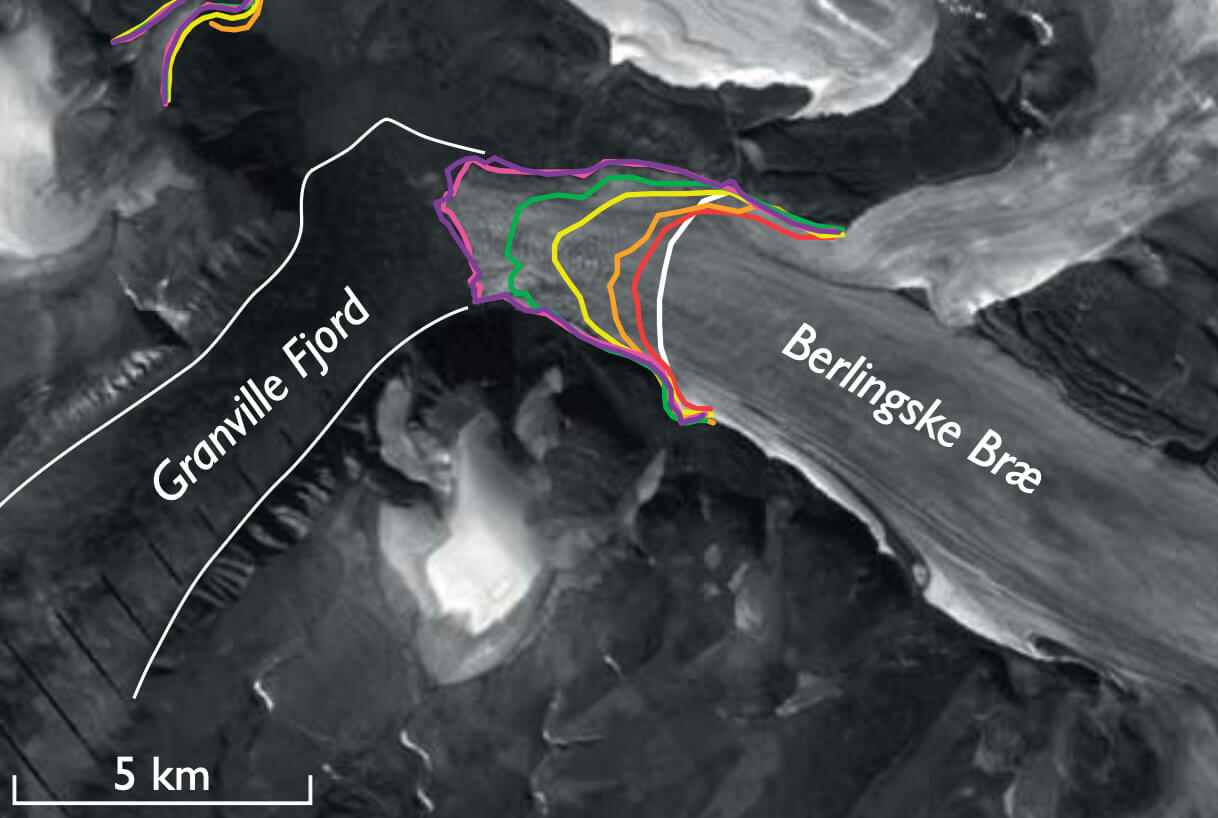
Greenland is receiving unprecedented international attention, both in scientific and political circles. Characterised by a central ice sheet up to 3.4 km thick (Inland Ice), numerous ice caps and hundreds of outlet glaciers debouching into the surrounding oceans, Greenland supports the second largest ice mass in the world. Analysis of glacier movements, melt rates and ice loss to the sea, provide data with which to assess mass balance changes and thereby predict global sealevel rise. Thus Greenland plays a central role in the current worldwide debate on climate change. Present-day dynamic ice loss is invariably advertised by the fast moving glaciers of western Greenland with their spectacular calf ice production, such as the ice streams around Disko Bugt reviewed by Weidick & Bennike (2007). This tends to overshadow ice stability and expansion seen in the form of stationary and advancing glaciers elsewhere in Greenland (MODIS 2009). While the seawards acceleration of glacier flow and retreat in frontal positions can be readily attributed to a shift in atmospheric and oceanic conditions (global warming), the same explanation can hardly be used for glaciers with contrasting movement histories.
How to Cite
Share
Copyright (c) 2010 Peter R. Dawes, Dirk van As

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Edited by Ole Bennike, Adam A. Garde and W. Stuart Watt
This Review of Survey activities presents a selection of 23 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, from the microscopic to the plate-tectonic level. In addition, an obituary about the former director of the [...]









