How to Cite
Share
Abstract
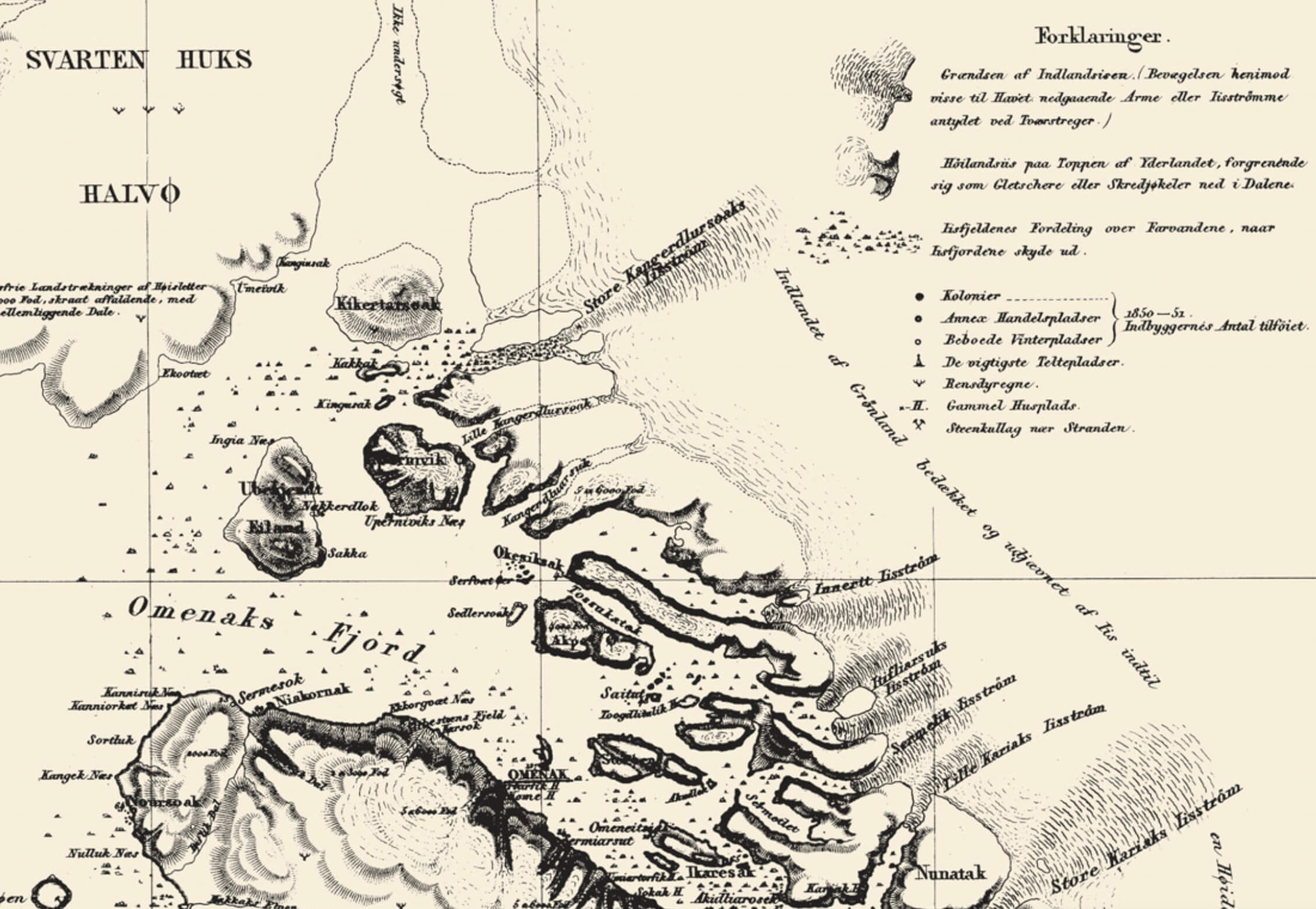
The Disko Bugt region in central West Greenland is characterised by permanent ice streams, of which Jakobshavn Isbræ is by far the most important. The first thorough studies on the glaciology of the region were conducted over 150 years ago by H.J. Rink, who introduced the terms 'ice streams' and 'Inland Ice'. Rink's work inspired new field work, which has continued to the present, and the long series of observations are unique for an Arctic region.
Cooling during the Cenozoic led to ice-sheet growth in Greenland. A number of interglacial occurrences have been reported from the Disko Bugt region, and during the penultimate glacial stage, the Greenland ice-sheet margin extended to the shelf break. During the last glacial maximum, the ice margin probably extended only to the inner part of the banks on the continental shelf, and large floating glaciers may have been present at this time. During the Younger Dryas cold period, the ice margin may have been located at a marked basalt escarpment west of Disko Bugt.
Disko Bugt was deglaciated rapidly in the early Holocene, around 10 500–10 000 years before present (10.5–10 ka B.P.), but when the ice margin reached the eastern shore of the bay, recession paused, and major moraine systems were formed. With renewed recession, the present ice-margin position was attained around 8–6 ka B.P., and by c. 5 ka B.P. the ice margin was located east of its present position. The subsequent Neoglacial readvance generally reached a maximum during the Little Ice Age, around AD 1850. This was followed by recession that has continued to the present day.
The relative sea-level history shows a rapid sea-level fall in the early Holocene, and a slow rise in the late Holocene. This development mainly reflects a direct isostatic response to the ice-margin history.
Jakobshavn Isbræ is the main outlet from the Greenland ice sheet. It drains c. 6.5% of the present Inland Ice, and produces c. 35–50 km3 of icebergs per year, corresponding to more than 10% of the total output of icebergs from the Inland Ice. The velocity of the central part of the ice stream at the front has been around 7 km/year since records began, but has nearly doubled in recent years. Other calf-ice producing glacier outlets in Disko Bugt produce c. 18 km3 per year. The large calf-ice production of Jakobshavn Isbræ may have been initiated at about 8 ka B.P. when the glacier front receded from the iceberg bank (Isfjeldsbanken) near Ilulissat. Ice streams in inner and outer Egedesminde Dyb may have been active during the early Holocene and during the last glacial maximum.
How to Cite
Share
Supplementary Files
Downloads
Anker Weidick and Ole Bennike
"Der Jakobshavner Eisstrom ist der König unter
Den grönlandischen Gletschern. Kein anderer der
Schnellaufenden Inlandeis-Abflüsse füllt so wie er
Seinen Fjord mit Eisberge an."
(Alfred Wegener 1930)
Central West Greenland is characterised by a number of permanent ice streams, a term introduced by H.J. Rink, who conducted the first glaciological investigations [...]










