How to Cite
Share
Abstract
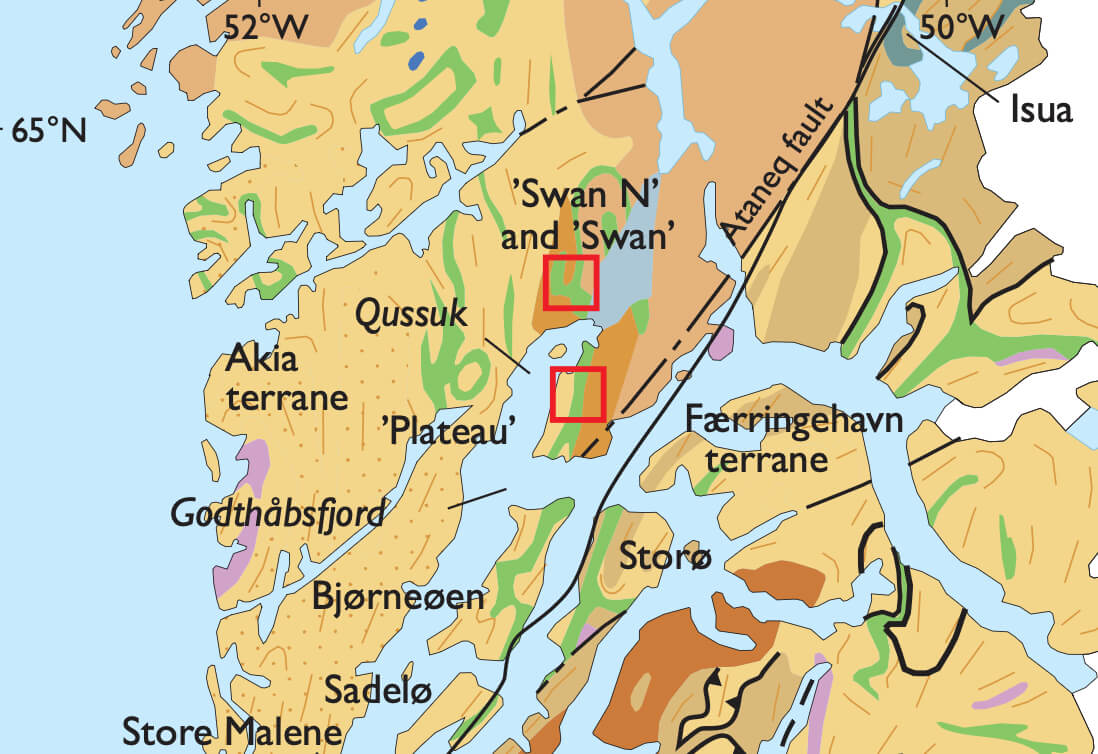
Gold exploration in the Godthåbsfjord region has been carried out since the early 1990s, and the region is now recognised as a gold province. Several prospects have been drilled and Storø is the most advanced project in the Færingehavn terrane. The gold occurrence at Storø is 2635 Ma old according to 207Pb/206Pb age determinations of metamorphic zircons associated with auriferous arsenopyrite (Nutman et al. 2007). Qussuk is located in the Akia terrane (Fig. 1), separated from the Færingehavn terrane in the south by the SW–NE-trending Ivinnguit fault. The Ivinnguit and Ataneq faults are spatially associated with several hydrothermal gold occurrences. From north to south these are: Isua, Storø, Bjørneøen, Sadelø, Store Malene and Qilanngaarsuit (Fig. 1; Appel et al. 2005; Kolb et al. 2009). The Qussuk prospect 20–25 km north of the Ataneq fault is 20 km long, 2–3 km wide, and divided from north to south into the ‘Swan N’, ‘Swan’ and ‘Plateau’ areas (Fig. 1).
How to Cite
Share
Copyright (c) 2010 Denis Martin Schlatter, Rasmus Christensen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Edited by Ole Bennike, Adam A. Garde and W. Stuart Watt
This Review of Survey activities presents a selection of 23 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, from the microscopic to the plate-tectonic level. In addition, an obituary about the former director of the [...]









