How to Cite
Share
Abstract
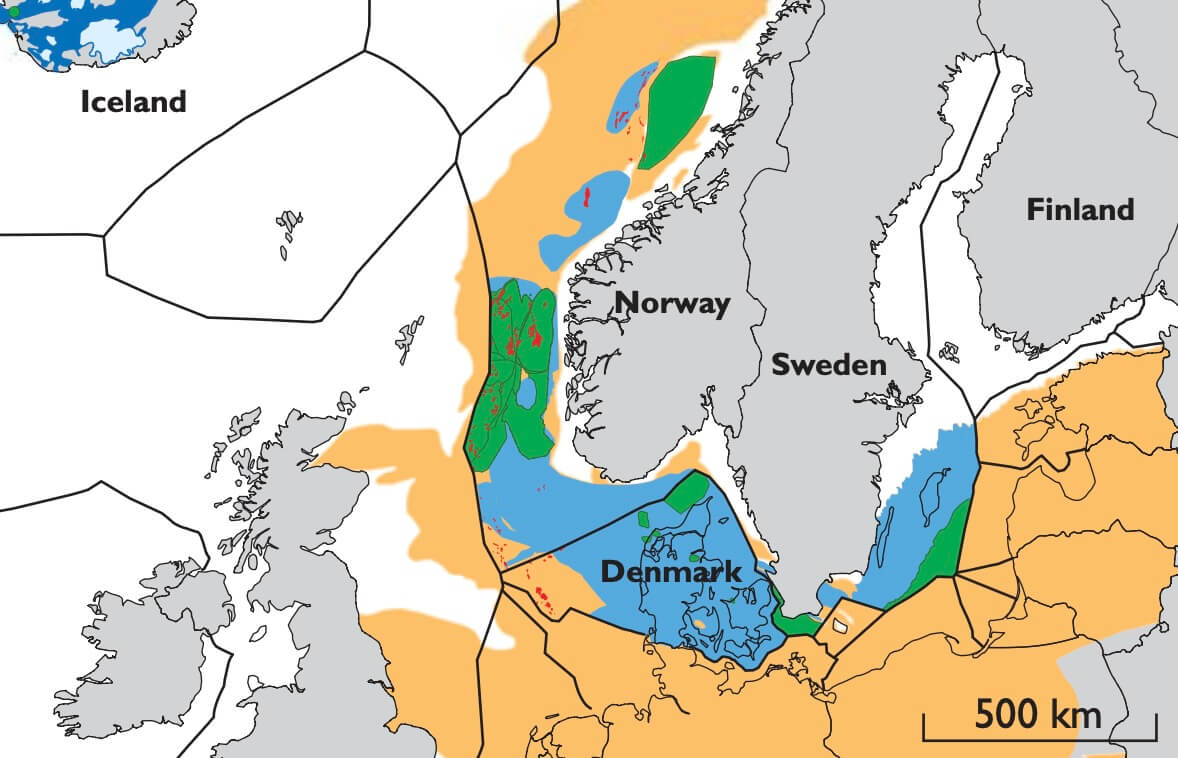
The concept of utilising available pore space in deep saline sandstone aquifers for storage of CO2 was recognised in the late 1980s. In 1996, the first commercial CO2 storage project began with injection into sandstones of the Utsira Formation in Norway. The formation is located above the Sleipner Formation from where the Sleipner field produces natural gas. The project was initiated due to a high CO2 content of the natural gas, which was subjected to a Norwegian offshore carbon tax. The natural gas is produced on the Sleipner platform where the CO2 is separated, captured and reinjected from a neighbouring platform. The potential for using the technology to reduce CO2 emissions from large stationary point sources initiated many research projects aimed at mapping areas with potential CO2 storage capacity around the world.
How to Cite
Share
Copyright (c) 2016 Karen Lyng Anthonsen, Peter Frykman, Carsten Møller Nielsen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Editors Adam A. Garde, Ole Bennike, Kristine Thrane and W. Stuart Watt
This issue of Review of Survey Activities presents a selection of 24 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of current activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, from the microscopic to the plate-tectonic level.
The Survey’s activities in Denmark are illustrated [...]









