How to Cite
Share
Abstract
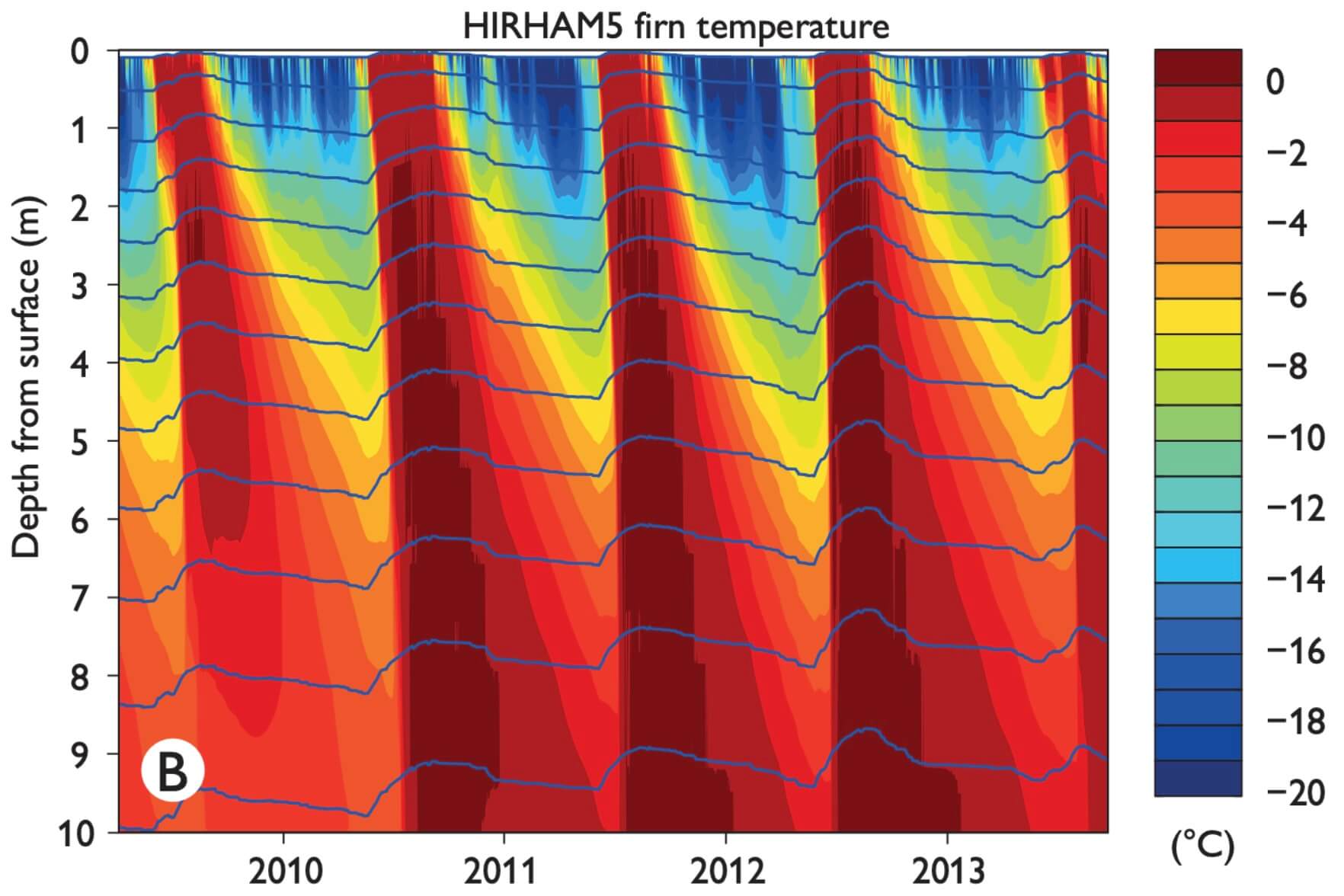
Recent record-warm summers in Greenland (Khan et al. 2015) have started affecting the higher regions of the ice sheet (i.e. the accumulation area), where increased melt has altered the properties of firn (i.e. multi-year snow). At high altitudes, meltwater percolates in the porous snow and firn, where it refreezes. The result is mass conservation, as the refrozen meltwater is essentially stored (Harper et al. 2012). However, in some regions increased meltwater refreezing in shallow firn has created thick ice layers. These ice layers act as a lid, and can inhibit meltwater percolation to greater depths, causing it to run off instead (Machguth et al. 2016). Meltwater at the surface also results in more absorbed sunlight, and hence increased melt in the accumulation area (Charalampidis et al. 2015). These relatively poorly understood processes are important for ice-sheet mass-budget projections.
How to Cite
Share
Copyright (c) 2016 Charalampos Charalampidis, Dirk van As, Peter L Langen, Robert S Fausto, Baptiste Vandecrux, Jason E Box

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Editors Adam A. Garde, Ole Bennike, Kristine Thrane and W. Stuart Watt
This issue of Review of Survey Activities presents a selection of 24 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of current activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, from the microscopic to the plate-tectonic level.
The Survey’s activities in Denmark are illustrated [...]









