How to Cite
Share
Abstract
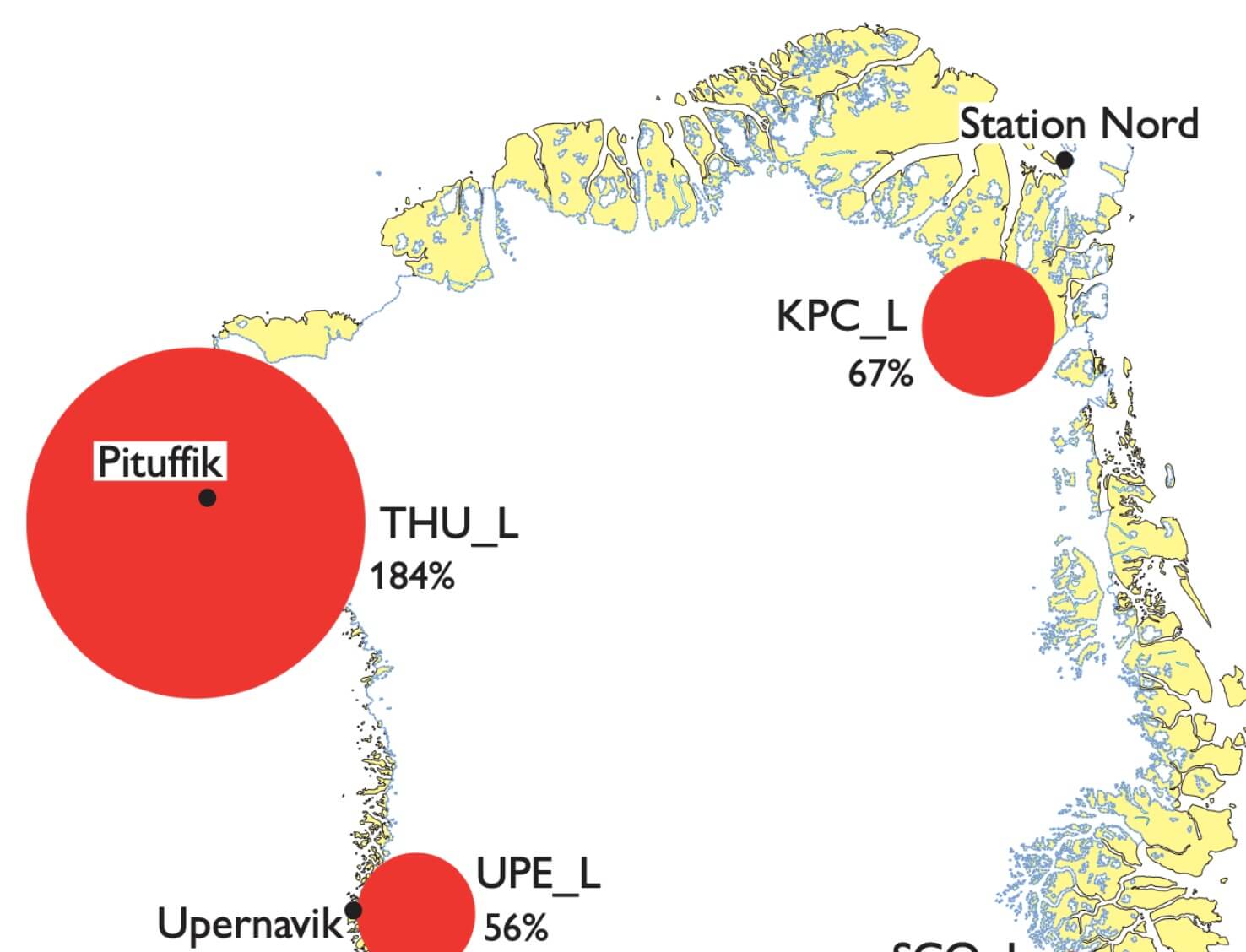
In recent years, the Greenland ice sheet has been losing mass at an average rate of 262 ± 21 Gt yr–1 (2007–2011; Andersen et al. 2015). Part of this mass loss was due to increases in melt, reducing the surface mass budget (Enderlin et al. 2014). Also, the acceleration of many marine-terminating outlet glaciers increased the dynamic mass loss (Rignot et al. 2008). Both mass-loss mechanisms are linked to recent increases in atmospheric and oceanic temperatures (Dutton et al. 2015). For instance, in summer 2012 Greenland experienced exceptionally warm atmospheric conditions, causing nearly the entire ice-sheet surface to melt for two periods of several days (Nghiem et al. 2012) and contributing to the largest annual ice-sheet mass loss on record (Khan et al. 2015). This is in contrast to a return to more average conditions in 2015 (Tedesco et al. in press).
How to Cite
Share
Copyright (c) 2016 Dirk van As, Robert S Fausto, John Cappelen, Roderik S W l van de Wa, Roger J Braithwaite, Horst Machguth, * PROMICE project team

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Editors Adam A. Garde, Ole Bennike, Kristine Thrane and W. Stuart Watt
This issue of Review of Survey Activities presents a selection of 24 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of current activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, from the microscopic to the plate-tectonic level.
The Survey’s activities in Denmark are illustrated [...]









