How to Cite
Share
Abstract
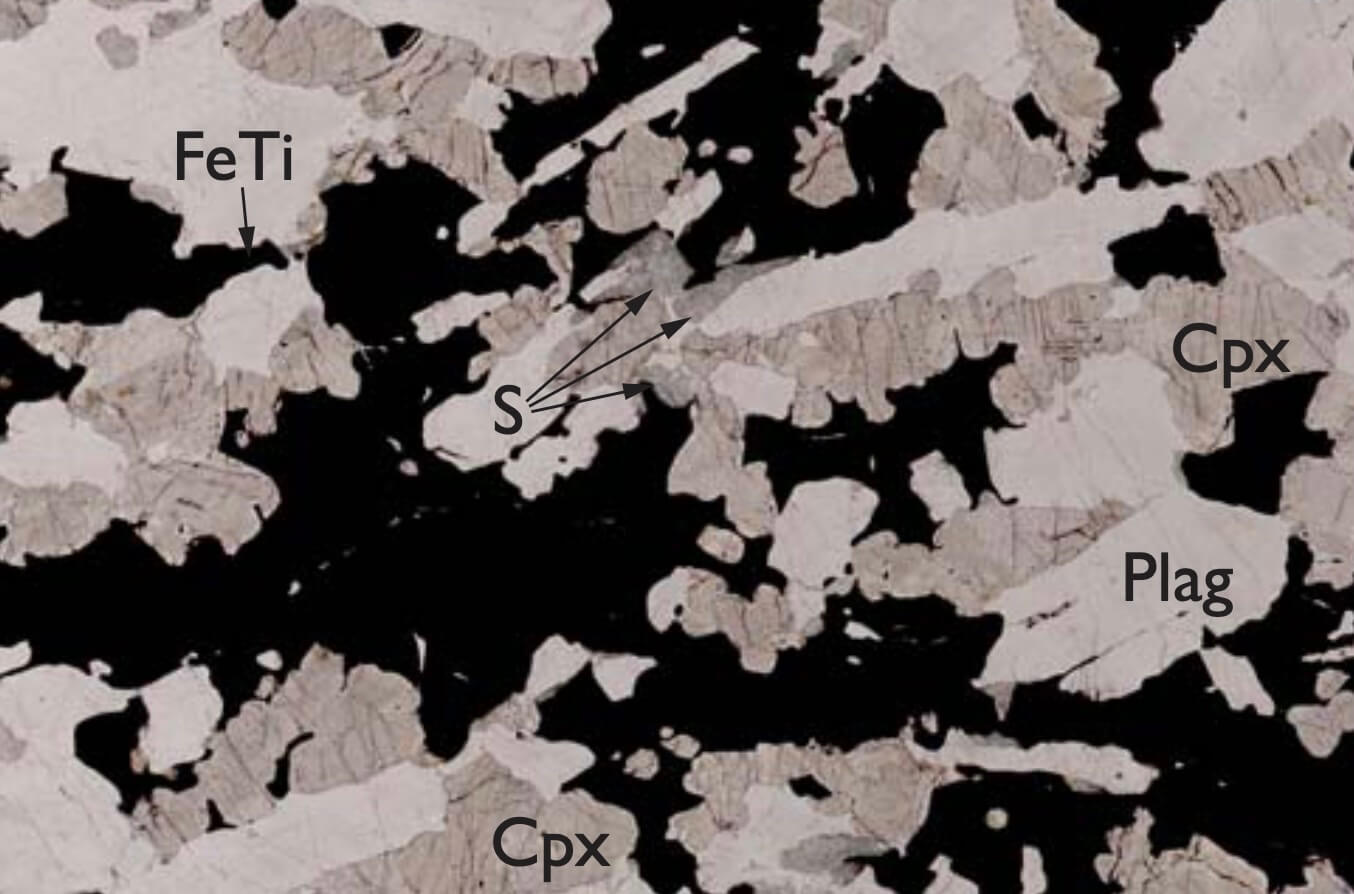
For more than 80 years the Skaergaard intrusion, 68°N in southern East Greenland, has been a foremost natural laboratory for the study of the crystallisation and fractionation of basaltic magma. This process has been of prime importance in the evolution of the Earth and other stony planets. Models that have been developed and refined during numerous studies of this particular intrusion have been part of the foundation for petrogenetic modelling for decades. In later years, vast amounts of new data have been added, due to systematic sampling in the field and from analysis of exploration drill cores. Methods for the study on grain-size scale have advanced, and the quest for a wellsupported genetic model for the PGE-Au mineralisation of the intrusion has intensified. The new data and insight question the applicability of conventional petrogenetic modelling, and as a consequence, increasing importance is placed on in situ crystallisation and fractionation in mush zones at the roof, walls and floor of the intrusion.
How to Cite
Share
Copyright (c) 2016 Troels F.D. Nielsen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Editors Adam A. Garde, Ole Bennike, Kristine Thrane and W. Stuart Watt
This issue of Review of Survey Activities presents a selection of 24 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of current activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, from the microscopic to the plate-tectonic level.
The Survey’s activities in Denmark are illustrated [...]









