How to Cite
Share
Abstract
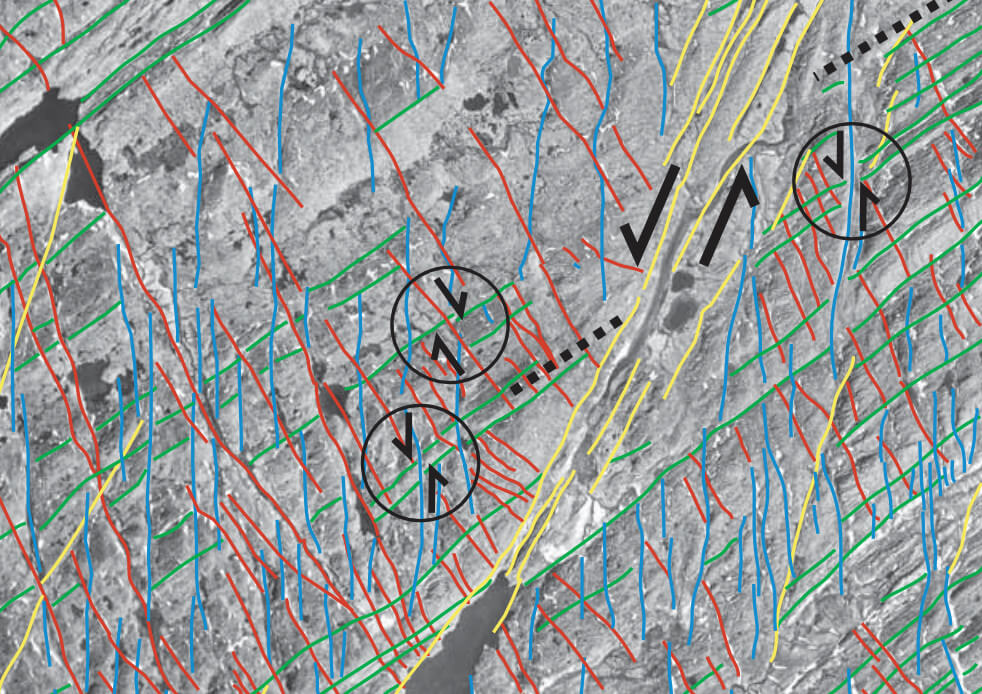
The complex Ungava fault zone lies in the Davis Strait and separates failed spreading centres in the Labrador Sea and Baffin Bay. This study focuses on coastal exposures east of the fault-bound Sisimiut basin, where the onshore expressions of these fault systems and the influence of pre-existing basement are examined. Regional lineament studies identify five main systems: N–S, NNE–SSW, ENE–WSW, ESE–WNW and NNW–SSE. Field studies reveal that strike-slip movements predominate, and are consistent with a ~NNE–SSW-oriented sinistral wrench system. Extensional faults trending N–S and ENE–WSW (basement-parallel), and compressional faults trending E–W, were also identified. The relative ages of these fault systems have been interpreted using cross-cutting relationships and by correlation with previously identified structures. A two-phase model for fault development fits the development of both the onshore fault systems observed in this study and regional tectonic structures offshore. The conclusions from this study show that the fault patterns and sense of movement on faults onshore reflect the stress fields that govern the opening of the Labrador Sea – Davis Strait – Baffin Bay seaway, and that the wrench couple on the Ungava transform system played a dominant role in the development of the onshore fault patterns.
How to Cite
Share
Downloads
Editors: A.A. Garde and F. Kalsbeek
Central West Greenland exposes a large region of Archaean continental crust that was rifted and subsequently reworked in the Palaeoproterozoic during the Nagssugtoqidian and Rinkian orogenies. The southern margin of the Nagssugtoqidian orogen with its deformed Kangâmiut dykes is a classic example of an orogenic [...]










