How to Cite
Share
Abstract
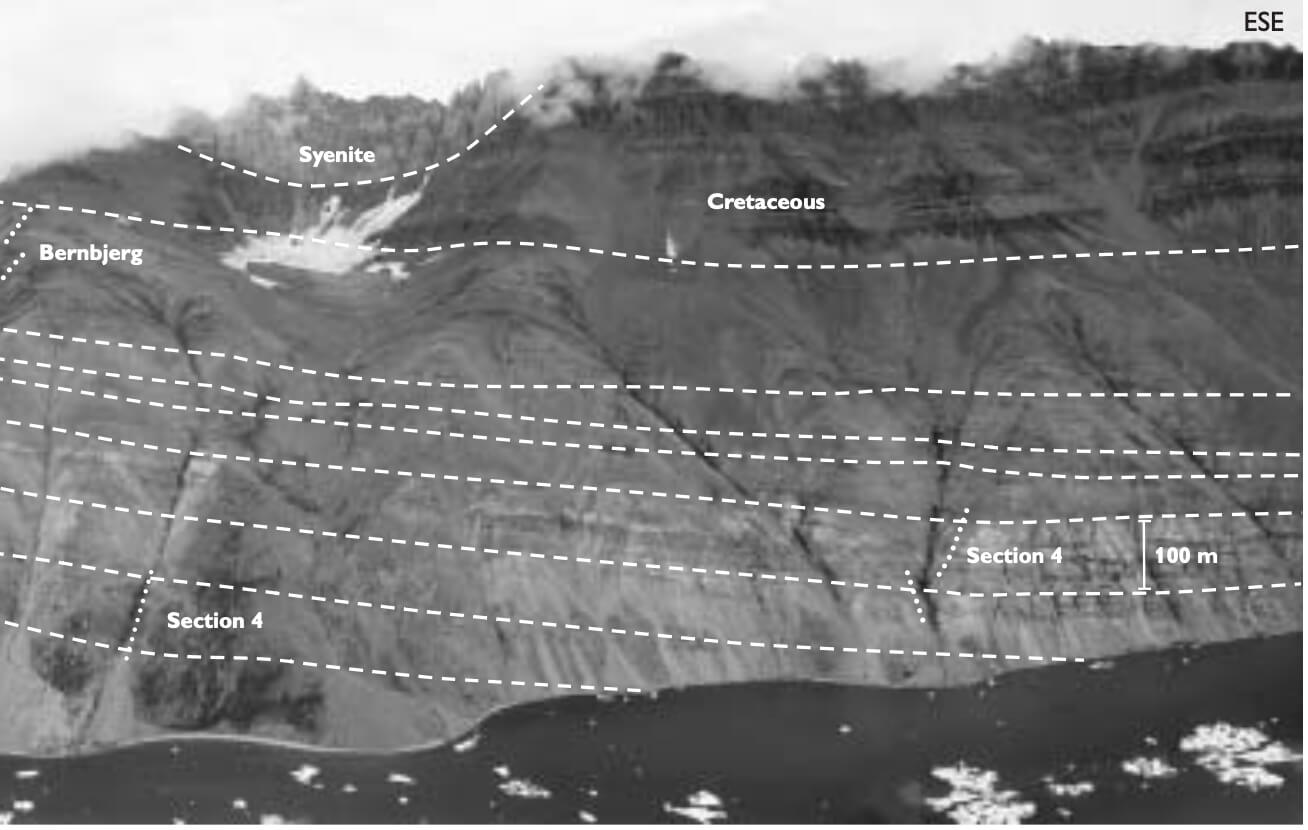
Middle–Late Jurassic rifting in East Greenland was marked by westwards tilting of wide fault blocks bounded by major N–S-trending east-dipping synthetic faults. The syn-rift successions thicken westwards towards the faults and shallow marine sandstones show mainly southwards axial transport directions. An exception to this general pattern is found in south-east Traill Ø, which constitutes the E-tilted Bjørnedal Block, which is bounded to the west by the westwards-dipping antithetic Vælddal Fault. The stratigraphic development of the Jurassic succession on this block shows important differences to the adjacent areas reflecting a different tectonic development. Shallow marine sand seems initially to have filled accommodation space of the immediately adjacent block to the west. This block subsequently acted as a bypass area and much of the sediment was spilled eastwards onto the hangingwall of the east-dipping Bjørnedal Block. The succession on the Bjørnedal Block shows an eastwards proximal–distal decrease in sandstone– mudstone ratio, reflecting increasing water depth and progressive under-filling of the subbasin towards the east in agreement with the dip direction of the fault block. The transverse, mainly south-eastwards palaeocurrents, the eastwards increase in water depths and decrease in sandstone–mudstone ratio on the Bjørnedal Block are at variance with the standard picture of west-tilted blocks with southwards-directed palaeocurrents and decrease in grain size. Earlier palaeogeographic reconstructions have to be modified to account for the east-dipping hangingwall and different stratigraphic development of the area. The sea was thus open towards the east and there is no direct indication of a barrier or shoal east of Traill Ø.
How to Cite
Share
Downloads
Edited by L. Stemmerik and S. Stouge
The Jurassic rift succession of East Greenland has been intensely studied over the last 25 years, particularly within the main outcrop areas of Jameson Land and Wollaston Forland. The more isolated and poorly known outcrops on Traill Ø, Hold with Hope, Hochstetter Forland and [...]










