How to Cite
Share
Abstract
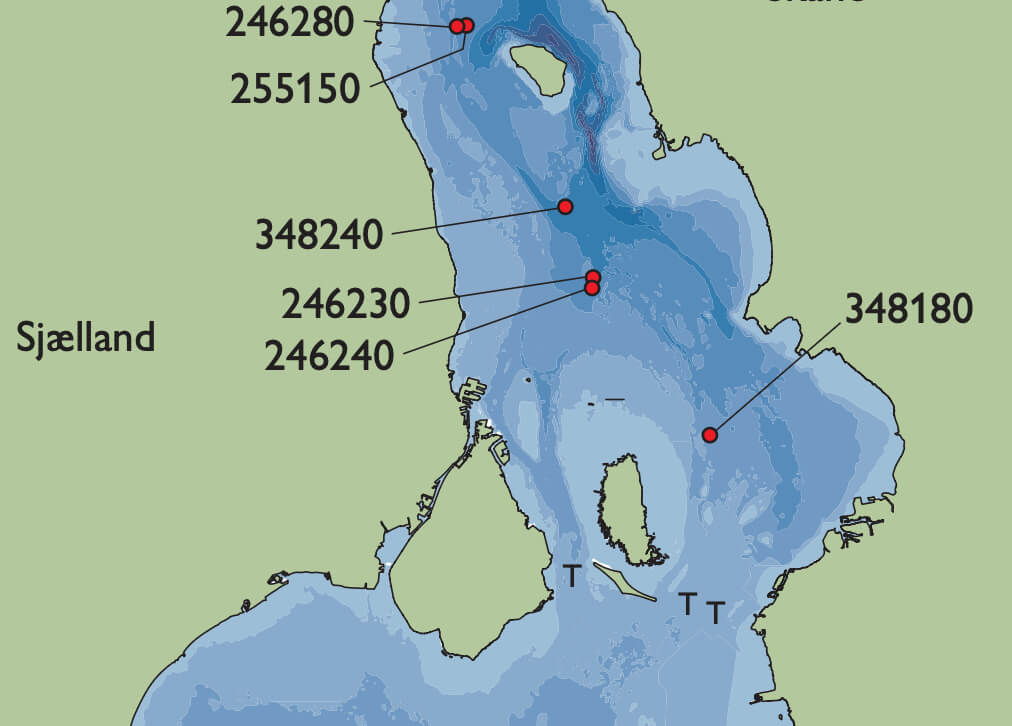
The Baltic Sea and Kattegat are connected via three straits: Storebælt, Lillebælt and Øresund (Fig. 1). Øresund is the shallowest with a threshold around 7 m deep and increasing water depths to the north (Fig. 2). In the early Holocene, global sea-level rise led to reflooding of Øresund. It started in northern Øresund which was transformed into a fjord. However, so far the timing of the transgression has not been well determined, but sediment cores collected north of the threshold, at water depths of 12 to 20 m, and a new series of radiocarbon ages help to constrain this. As the relative sea level continued to rise, the threshold in Øresund was also flooded, and Øresund became a strait. In mid-Holocene time, the relative sea level rose until it was 4–5 m higher than at present, and low-lying areas around Øresund became small fjords. During the late Holocene, the relative sea level fell again. Part of the data set discussed here was presented by Andreasen (2005).
How to Cite
Share
Copyright (c) 2012 Ole Bennike, Martin Skov Andreasen, Jørn Bo Jensen, Matthias Moros, Nanna Noe-Nygaard

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Edited by Ole Bennike, Adam A. Garde and W. Stuart Watt
This Review of Survey activities presents a selection of 20 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, from the microscopic to the plate-tectonic level.
The Survey's activities in Denmark and surrounding areas are illustrated by [...]









