How to Cite
Share
Abstract
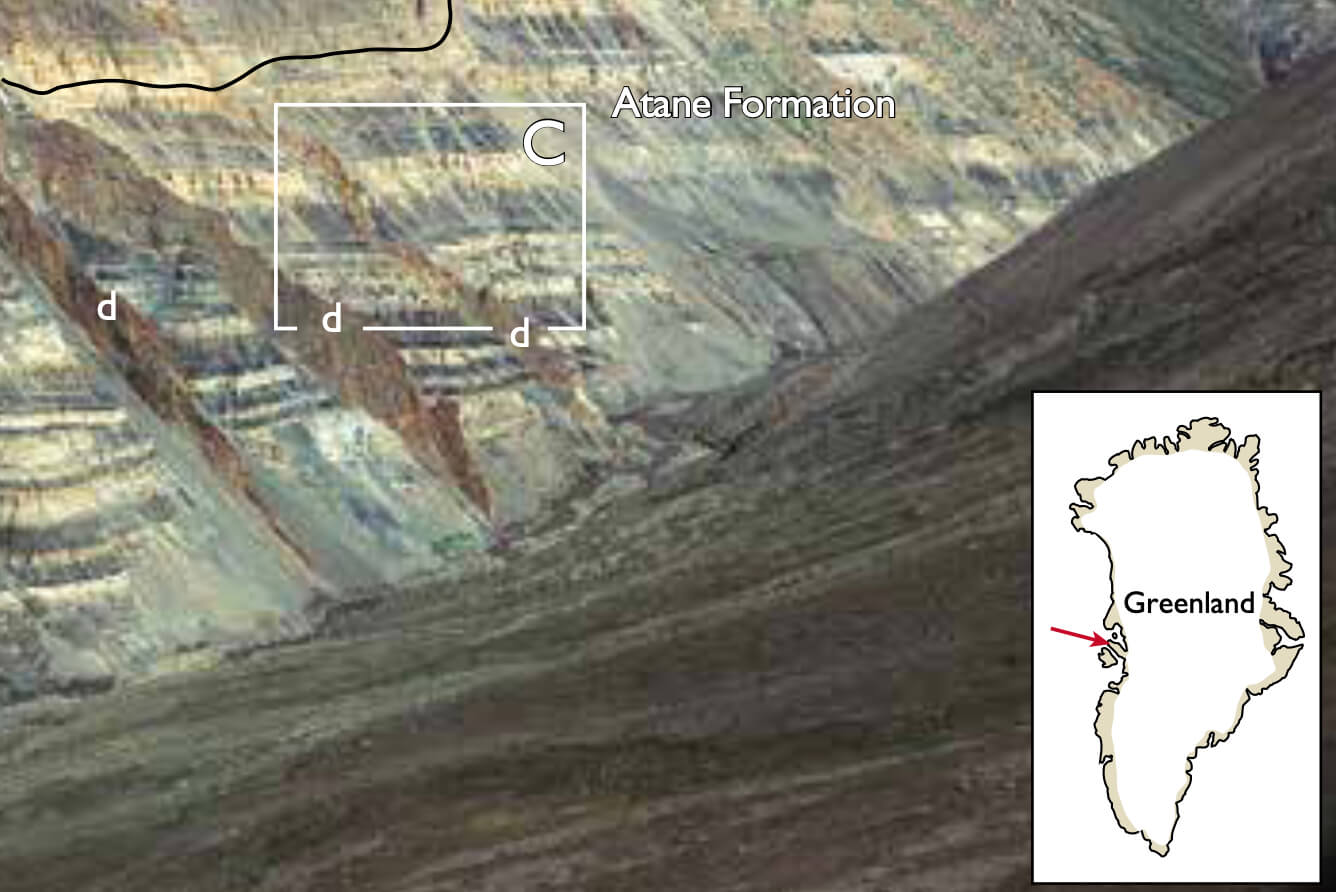
Gamma-ray logs are widely used as a lithology indicator in wells as part of standard petrophysical interpretations. In cored wells, gamma-ray logs should always be calibrated to the lithology in order to correct the petrophysical model. Gamma radiation is emitted from three elements, K, Th and U (potassium, thorium and uranium) which occur in minerals such as feldspar, mica, glauconite, clay minerals, zircon, titanite and apatite as well as in organic complexes. Organic-rich mudstones usually have high gamma-radiation values and quartz-rich sandstones low values. In many places, upward-coarsening successions are recognisable from the gamma log. The gamma log records the sum of radiation from K, Th and U, and their relative contributions are measured in a spectral gamma-ray log. The present case study focuses on spectral gamma-ray characterisation of the deltaic Atane Formation which shows well-developed, upward-coarsening delta-front deposits in outcrops (Fig. 1C).
How to Cite
Share
Copyright (c) 2013 Gunver Krarup Pedersen, Niels H Schovsbo, Henrik Nøhr-Hansen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Downloads
Edited by Ole Bennike, Adam A. Garde and W. Stuart Watt
This Review of Survey activities presents a selection of 17 papers reflecting the wide spectrum of activities of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, from the microscopic to the plate-tectonic level.
The Survey's activities in Denmark and surrounding areas are [...]









