How to Cite
Share
Abstract
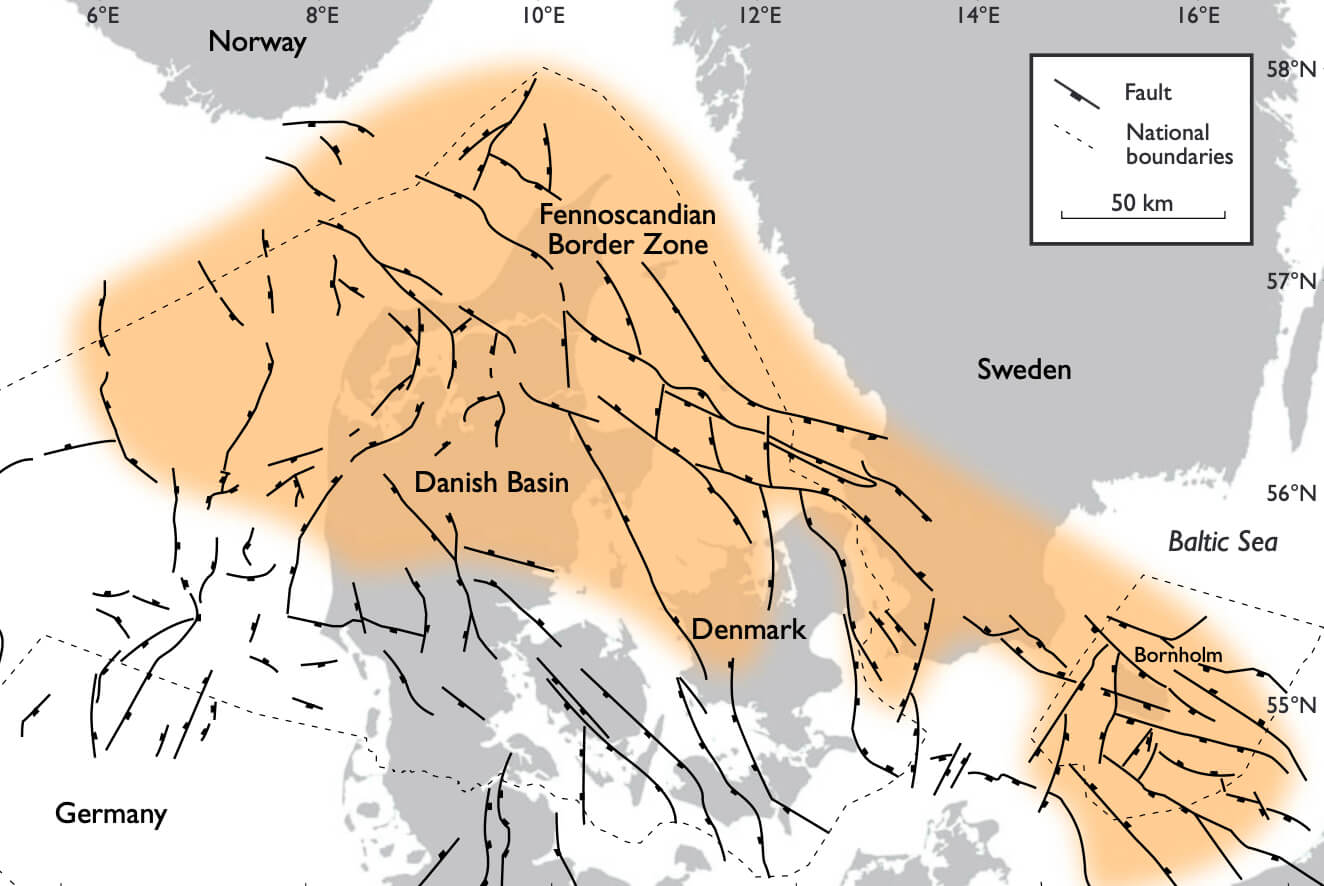
In the Kattegat area, Denmark, the Sorgenfrei–Tornquist Zone, an old crustal weakness zone, was repeatedly reactivated during Triassic, Jurassic and Early Cretaceous times with dextral transtensional movements along the major boundary faults. These tectonic events were minor compared to the tectonic events of the Late Carboniferous – Early Permian and the Late Cretaceous – Early Tertiary, although a dynamic structural and stratigraphic analysis indicates that the Sorgenfrei–Tornquist Zone was active compared to the surrounding areas. At the end of the Palaeozoic, the area was a peneplain. Regional Triassic subsidence caused onlap towards the north-east, where the youngest Triassic sediments overlie Precambrian crystalline basement. During the Early Triassic, several of the major Early Permian faults were reactivated, probably with dextral strike-slip along the Børglum Fault. Jurassic – Early Cretaceous subsidence was restricted primarily to the area between the two main faults in the Sorgenfrei–Tornquist Zone, the Grenå–Helsingborg Fault and the Børglum Fault. This restriction of basin development indicates a change in the regional stress field at the Triassic–Jurassic transition. Middle Jurassic and Late Jurassic – Early Cretaceous subsidence followed the Early Jurassic pattern with local subsidence in the Sorgenfrei–Tornquist Zone, but now even more restricted to within the zone. The subsidence showed a decrease in the Middle Jurassic, and increased again during Late Jurassic – Early Cretaceous times. Small faults were generated internally in the Sorgenfrei–Tornquist Zone during the Mesozoic with a pattern that indicates a broad transfer of strike-slip/oblique-slip motion from the Grenå–Helsingborg Fault to the Børglum Fault.
How to Cite
Share
Downloads
Editors: Jon R. Ineson and Finn Surlyk
The Jurassic rocks of Denmark and East Greenland record the evolution of two discrete portions of the Mesozoic rift complex, now separated by the North Atlantic Ocean. The Jurassic of Denmark and adjacent areas occurs mostly in the subsurface and research has thus focussed [...]










