How to Cite
Share
Abstract
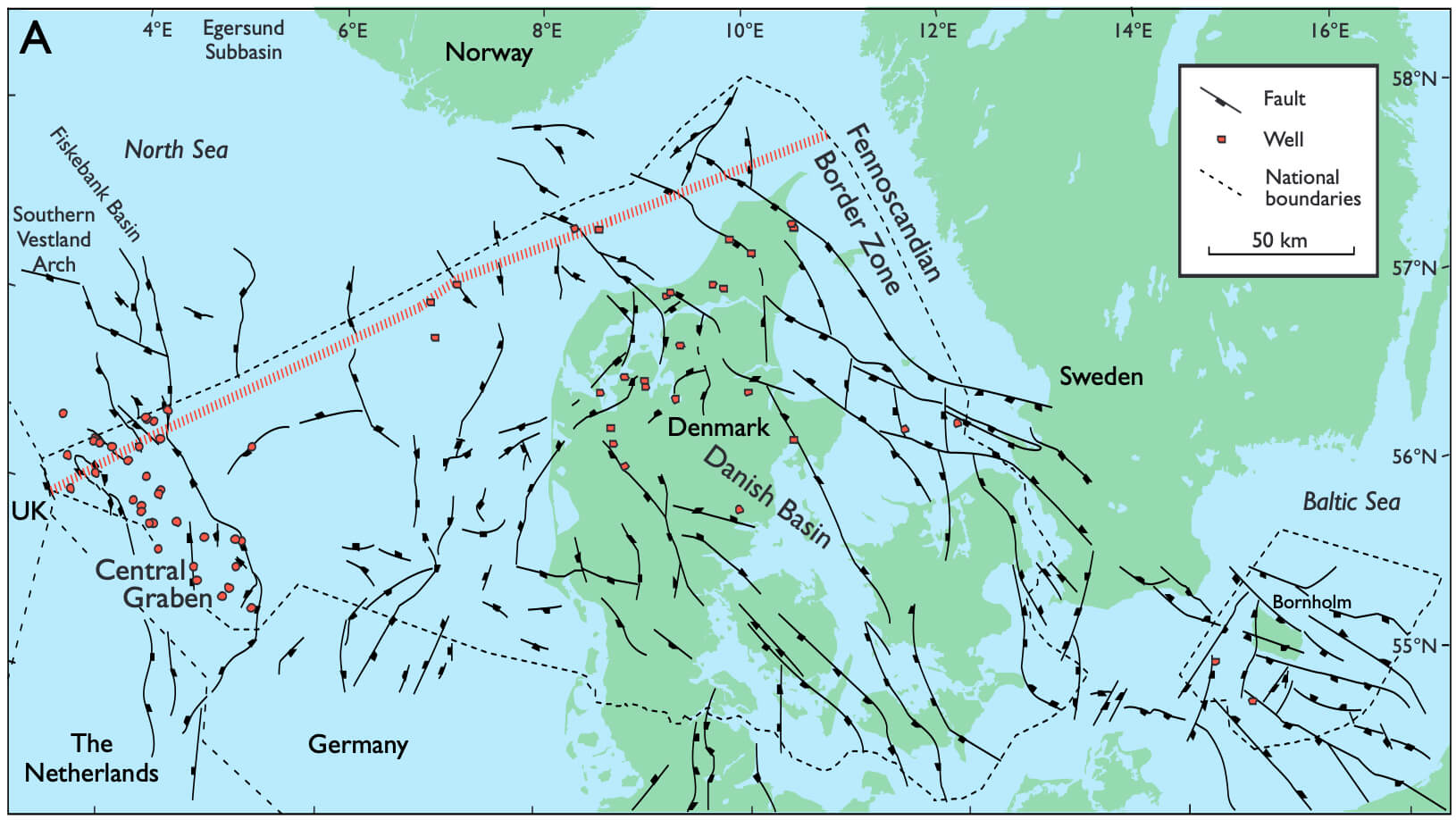
A complete updated and revised lithostratigraphic scheme for the Jurassic succession of the onshore and offshore Danish areas is presented together with an overview of the geological evolution. The lithostratigraphies of Bornholm, the Danish Basin and the Danish Central Graben are described in ascending order, and a number of new units are defined. On Bornholm, the Lower–Middle Jurassic coal-bearing clays and sands that overlie the Lower Pliensbachian Hasle Formation are referred to the new Sorthat Formation (Lower Jurassic) and the revised Bagå Formation (Middle Jurassic). In the southern Danish Central Graben, the Middle Jurassic succession formerly referred to the Lower Graben Sand Formation is now included in the revised Bryne Formation. The Lulu Formation is erected to include the uppermost part of the Middle Jurassic succession, previously referred to the Bryne Formation in the northern Danish Central Graben. The Upper Jurassic Heno Formation is subdivided into two new members, the Gert Member (lower) and the Ravn Member (upper). The organic-rich part of the upper Farsund Formation, the former informal ‘hot unit’, is established formally as the Bo Member. Dominantly shallow marine and paralic deposition in the Late Triassic was succeeded by widespread deposition of offshore marine clays in the Early Jurassic. On Bornholm, coastal and paralic sedimentation prevailed. During maximum transgression in the Early Toarcian, sedimentation of organic-rich offshore clays took place in the Danish area. This depositional phase was terminated by a regional erosional event in early Middle Jurassic time, caused by uplift of the central North Sea area, including the Ringkøbing–Fyn High. In the Sorgenfrei–Tornquist Zone to the east, where slow subsidence continued, marine sandy sediments were deposited in response to the uplift. Uplift of the central North Sea area was followed by fault-controlled subsidence accompanied by fluvial and floodplain deposition during Middle Jurassic time. On Bornholm, deposition of lacustrine muds, fluvial sands and peats dominated. The late Middle Jurassic saw a gradual shift to shallow marine deposition in the Danish Central Graben, the Danish Basin and Skåne, southern Sweden. During the Late Jurassic, open marine shelf conditions prevailed with deposition of clay-dominated sediments while shallow marine sands were deposited on platform areas. The Central Graben received sand by means of sediment gravity flows. The clay sediments in the Central Graben became increasingly rich in organic matter at the Jurassic–Cretaceous transition, whilst shallow marine coarse-grained deposits prograded basinwards in the Sorgenfrei– Tornquist Zone.
How to Cite
Share
Downloads
Editors: Jon R. Ineson and Finn Surlyk
The Jurassic rocks of Denmark and East Greenland record the evolution of two discrete portions of the Mesozoic rift complex, now separated by the North Atlantic Ocean. The Jurassic of Denmark and adjacent areas occurs mostly in the subsurface and research has thus focussed [...]










